Land Use Science in Action

CONTINUED FOREST PROTECTION MUST BE CORE TO COMMUNITY DEVELOPMENT
- Marginal lands are now being used for crop production to feed an ever-growing population.
- Agriculture productivity must increase to meet demand, intensification rather than intensification.
- Currently, an urgent need exists for information to maximize yield based on land capabilities to mitigate land degradation, improve productivity, and to alleviate food insecurity.
- NASA's role in Earth observation is essential for merging cutting-edge modeling with very high-resolution commercial data to inform the sustainability of current land use and food security.
- Long-term effects of a lack of land tenure rights can be addressed with multi-resolution remote sensing data to relieve land pressure and move toward sustainable management practices.
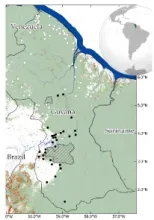
Village Sustainable Planning and its influence on tropical forestry outcomes in Guyana
CONTINUED FOREST PROTECTION MUST BE CORE TO COMMUNITY DEVELOPMENT
- Carbon payment mechanisms to incentive sustainable forest management have an impact on forest loss
- Analyses integrating remote sensing and socioeconomic data can quantify the effectiveness of Village Sustainability Planning program on forest and land use
- With the rise carbon payment mechanisms for forest conservation, urgent need for such analyses is needed to inform current and future sustainable planning
- NASA’s role in Earth observation is essential for measuring and monitoring global investments in carbon markets
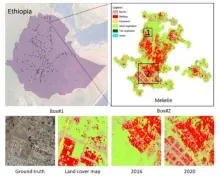
DISSECTING AND ANALYZING URBANIZATION PATTERNS AT MULTIPLE SCALES
- Rapid urbanization is occurring within secondary cities, particular in Africa, which need more data and analyses to understand how urban change in occurring and its implications.
- Secondary cities provide great socio-economic opportunities, but rapid growth creates challenges for management, sustainable development, and provisioning of resources.
- Multi-tiered approaches are needed to merge the monitoring of broad urbanization patterns with characterizations of heterogenous urban land cover within cities consistently.
- The current era of remote sensing technologies provides opportunities for multi-scale data fusions to analyze urbanization patterns and implications across scales.
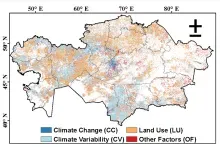
Inferential multi-stage multi-model framework to detect vegetation degradation
- Small ruminant and horse density explained 35% of vegetation degradation
- Increasing trends in hotspots of livestock density in the south-central and southeastern regions, whereas medium-density clusters in the northern and northwestern regions of KZ.
- Socioeconomic driver impacts were amplified when interacting with environmental drivers.
- Remote sensing combined with gridded socioeconomic data helps quantify anthropogenic impacts on vegetation degradation

ACTIONS AT DIFFERENT LEVELS ARE NEEDED TO MAKE AQUACULTURE MEET THE SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT GOALS AND ADAPT TO CLIMATE CHAGNES
- Aquaculture farming has expanded from coastal areas to near-coastal brackish-water and inland freshwater areas, and they widely adopts intensive farming technologies for higher yield.
- These cause issues such as increased soil salinization, water consumption and methane emission.
- Satellite remote sensing can provide unique and comprehensive mapping of aquaculture, including aquaculture-related landcover/use changes and aquaculture farming activities.
- Combined with technical and social surveys, the patterns of aquaculture changes can be revealed.
- Stronger actions at the national, regional, and farm levels are needed to regulate aquaculture intensification and expansion to meet the sustainable development goals (SDGs) and adapt to climate changes.
Pagination
- Page 1
- Next page